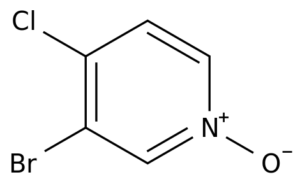
The development of advanced pharmaceuticals relies heavily on specialized chemical intermediates that act as building blocks in complex synthesis pathways. One such compound is 3-Bromo-4-chloropyridine 1-oxide (CAS: 99839-30-2), a halogenated pyridine derivative with growing importance in the pharmaceutical sector, particularly in oncology research and drug development.
Molecular Formula: C5H3BrClNO
Molecular Weight: ~208.4 g/mol
Structure: This compound is characterized by a pyridine ring with a bromine atom at the 3-position, chlorine at the 4-position, and an N-oxide functional group.
Properties: The presence of halogens and the N-oxide functionality imparts high reactivity, making it an ideal substrate for coupling reactions, substitutions, and functional group transformations.
The synthesis of oncology-related active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) often involves complex heterocyclic scaffolds. 3-Bromo-4-chloropyridine 1-oxide plays a pivotal role in this process due to:
Versatility in Functionalization
The bromine and chlorine atoms serve as handles for cross-coupling reactions (e.g., Suzuki, Heck, or Buchwald–Hartwig reactions), enabling the introduction of diverse functional groups.
The N-oxide functionality enhances the electronic properties of the pyridine ring, improving reactivity and selectivity in synthetic steps.
Building Block for Oncology Drug Candidates
Pyridine derivatives are a common motif in kinase inhibitors, anti-proliferative agents, and targeted therapies.
By modifying this intermediate, researchers can generate libraries of drug-like molecules for screening in oncology programs.
Facilitating SAR (Structure–Activity Relationship) Studies
The compound provides a robust starting point for analog development.
Fine-tuning substituents around the pyridine core helps optimize potency, selectivity, and pharmacokinetic profiles of oncology drug candidates.
Kinase Inhibitors: Many anticancer drugs target kinases; pyridine-based intermediates are vital for designing kinase-binding motifs.
Heterocyclic Drug Scaffolds: The pyridine N-oxide can be transformed into diverse heterocycles, broadening the chemical space explored in oncology.
Research Tool Compound: It is also used as a reagent for developing chemical probes in cancer biology.
The demand for reliable intermediates like 3-Bromo-4-chloropyridine 1-oxide is growing with the acceleration of oncology drug pipelines. Its stability, synthetic flexibility, and compatibility with modern organic synthesis make it a preferred intermediate for medicinal chemists working on next-generation cancer therapeutics.
In the race to develop more effective oncology treatments, specialized intermediates such as 3-Bromo-4-chloropyridine 1-oxide (CAS: 99839-30-2) play a crucial role. By enabling precise modifications and supporting the synthesis of complex drug candidates, this compound underscores the importance of fine-tuned chemical building blocks in advancing cancer research.