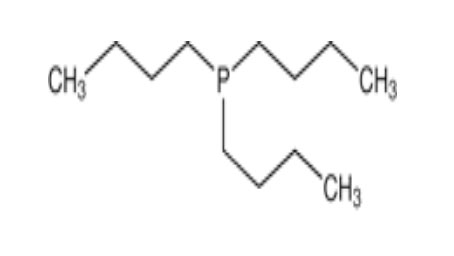
Tri-n-butylphosphine (CAS 998-40-3) is an organophosphorus compound widely recognized for its role as a ligand, catalyst component, and reducing agent in modern chemical synthesis. Known for its strong nucleophilicity and ability to coordinate effectively with transition metals, this compound plays a vital role in pharmaceuticals, polymer manufacturing, and fine chemical industries. Its versatility and chemical stability make it a preferred reagent for both laboratory research and large-scale industrial processes.
Tri-n-butylphosphine is a trialkylphosphine consisting of a phosphorus atom bonded to three n-butyl groups. It is typically a colorless to pale-yellow liquid with a strong, characteristic odor. Its high reactivity and powerful electron-donating ability make it one of the most commonly used phosphine ligands.
CAS Number: 998-40-3
Chemical Name: Tri-n-butylphosphine / Tributylphosphine
Molecular Formula: C12H27P
Category: Organophosphorus compound / Ligand / Catalyst component
Tri-n-butylphosphine exhibits several properties that make it valuable in diverse reactions:
Strong nucleophile due to electron-rich phosphorus
Efficient coordinating ligand for transition metals
High solubility in organic solvents
Reacts readily with alkyl halides, acids, and oxidizing agents
Liquid form facilitates handling and formulation
These characteristics enable it to serve as a powerful activator and reaction promoter in catalytic processes.
Tri-n-butylphosphine is widely used as a ligand in:
Palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions (Heck, Suzuki, Stille)
Carbon–carbon and carbon–heteroatom bond-forming reactions
Homogeneous catalysis for specialty fine chemical production
Its electron-donating ability stabilizes catalytic metal complexes and improves reaction efficiency.
In pharma synthesis, it is used to:
Prepare active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) intermediates
Facilitate selective organic transformations
Modify heterocyclic and aromatic frameworks
Enhance yields in multi-step synthesis routes
Its compatibility with sensitive reaction conditions makes it indispensable for complex drug development.
Tri-n-butylphosphine is also employed in:
Polymerization reactions
Modification of polymer chains
Production of specialty materials and functional coatings
Its reactivity supports precise control over polymer structure and molecular weight.
Chemical manufacturers utilize tributylphosphine for:
Reduction reactions
Alkylation and substitution chemistry
Preparation of phosphonium salts
Advanced R&D formulations
Its role in generating specialty intermediates makes it highly valuable for custom synthesis industries.
The increasing adoption of catalytic technologies in pharmaceutical and specialty chemical manufacturing has boosted the demand for tri-n-butylphosphine. Industries value its:
High performance as a catalytic ligand
Ability to increase reaction selectivity
Strong reducing capabilities
Cost-effectiveness in large-scale operations
As a result, the compound remains a vital part of the global organophosphorus chemical market.
Due to its reactivity, tri-n-butylphosphine must be handled carefully:
Avoid exposure to air and moisture, as it can oxidize
Use in a well-ventilated area
Wear protective gear (gloves, goggles, lab coat)
Store in tightly sealed containers under inert atmosphere
Refer to supplier MSDS for detailed safety instructions
Tri-n-butylphosphine (CAS 998-40-3) is a powerful and versatile chemical crucial to modern catalytic processes, pharmaceutical synthesis, and fine chemical development. Its strong nucleophilicity and exceptional ligand properties make it indispensable in both laboratory and industrial environments. As the demand for efficient catalytic systems and specialty chemicals continues to grow, tri-n-butylphosphine remains a cornerstone of advanced chemical manufacturing.