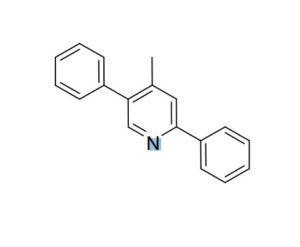
4-Methyl-2,5-diphenylpyridine (CAS No: 156021-08-8) is an aromatic heterocyclic compound that has gained significant attention in the fields of organic chemistry and materials science. Its unique pyridine backbone substituted with phenyl and methyl groups contributes to its stability, electronic properties, and potential utility as an intermediate in advanced chemical synthesis.
Chemical Name: 4-Methyl-2,5-diphenylpyridine
CAS Number: 156021-08-8
Molecular Formula: C₁₈H₁₅N
Molecular Weight: 245.32 g/mol
Chemical Structure: Contains a pyridine ring substituted with two phenyl groups (at the 2 and 5 positions) and one methyl group (at the 4 position).
Appearance: Generally a crystalline solid or powder
Solubility: Soluble in most organic solvents such as chloroform, dichloromethane, and ethanol.
The combination of aromatic rings and a nitrogen heteroatom gives this compound excellent conjugation and stability, making it suitable for use in both laboratory and industrial applications.
Thermal and Chemical Stability
4-Methyl-2,5-diphenylpyridine demonstrates excellent thermal and oxidative stability, which makes it suitable for high-temperature reactions and as a component in durable materials.
Aromaticity and Electron Delocalization
The presence of multiple aromatic rings enhances π–π conjugation, contributing to potential photophysical and electronic applications.
Versatile Reactivity
The nitrogen in the pyridine ring allows for coordination with metals, enabling its use in catalytic and organometallic chemistry.
This compound serves as a valuable intermediate in the preparation of complex organic molecules, including pharmaceuticals and fine chemicals. Its structure allows for selective functionalization and derivatization, making it a useful starting material for heterocyclic compound synthesis.
Due to its stable aromatic framework, 4-Methyl-2,5-diphenylpyridine is explored as a building block for organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), photoluminescent materials, and conductive polymers. Its electron-rich pyridine core can enhance charge transport and luminescent properties in such materials.
The pyridine nitrogen acts as a ligand in metal complex formation, facilitating applications in homogeneous catalysis and coordination chemistry. These metal complexes often show enhanced catalytic activity in oxidation and coupling reactions.
In academic and industrial research, this compound is employed to study pyridine-based derivatives, aromatic substitution mechanisms, and structure–property relationships in heterocycles.
While 4-Methyl-2,5-diphenylpyridine is relatively stable, standard laboratory precautions should be followed:
Handle under dry, well-ventilated conditions.
Avoid direct contact with skin and eyes.
Store in a tightly closed container away from strong oxidizing agents and direct sunlight.
Personal protective equipment such as gloves, goggles, and lab coats should always be used when handling this compound.
4-Methyl-2,5-diphenylpyridine (CAS No: 156021-08-8) stands out as a versatile compound with promising applications in organic synthesis, catalysis, and material science. Its stable pyridine core and aromatic substituents make it an essential building block for researchers developing new molecules and advanced materials. As industries increasingly explore heterocyclic compounds for high-performance applications, this compound continues to find expanding relevance in modern chemistry.