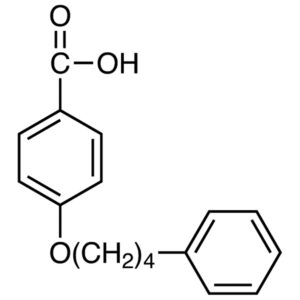
4-(4-Phenylbutoxy)benzoic Acid, known by its CAS number 30131-16-9, is an advanced organic compound widely used in specialty chemical research, pharmaceutical development, and material science. With its unique aromatic structure and functional groups, it serves as a valuable intermediate for producing high-performance materials and complex organic molecules.
In this article, we explore its characteristics, key applications, and the importance of this compound in modern industrial and scientific development.
4-(4-Phenylbutoxy)benzoic Acid is a substituted aromatic carboxylic acid, containing:
A benzoic acid core
A phenylbutoxy side chain
Multiple aromatic rings that enhance structural stability
Chemical Name: 4-(4-Phenylbutoxy)benzoic Acid
CAS Number: 30131-16-9
Molecular Formula: C17H18O3
Category: Organic intermediate / aromatic carboxylic acid
This combination of a carboxyl group and aromatic ether linkage makes it ideal for advanced chemical synthesis.
4-(4-Phenylbutoxy)benzoic Acid exhibits several important characteristics:
The dual aromatic structure ensures high thermal and structural stability, beneficial for chemical and material applications.
Containing both:
Carboxylic acid (–COOH)
Phenoxy linkage (–O–)
…makes it suitable for downstream reactions in fine chemical production.
It interacts well with organic solvents and blends easily into chemical reaction systems, making it efficient for multi-step research activities.
This compound is widely used as:
An intermediate for drug candidate molecules
A precursor for aromatic active substances
A component for designing bioactive frameworks
Its structural complexity helps researchers build advanced medicinal chemistry compounds.
Aromatic carboxylic acids like this one are used in:
Liquid crystal materials
Polymer additives
High-performance organic materials
Its rigid aromatic ring system supports stable mesogenic (liquid crystal-forming) structures.
4-(4-Phenylbutoxy)benzoic Acid is valued for:
Structure–activity relationship (SAR) studies
Building blocks for advanced organic frameworks
Laboratory-scale molecular design
It serves as a key intermediate in developing specialty chemicals.
Researchers utilize this compound to study:
Substituted aromatic reactivity
Ether-linked carboxylic acids
Molecular modeling and structural behavior
Its molecular design makes it ideal for educational and analytical research.
Like most organic laboratory chemicals, proper safety practices are essential.
Gloves
Lab coat
Protective eyewear
Adequate ventilation
Store in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area
Keep tightly sealed
Avoid heat and direct sunlight
Avoid inhalation of dust
Prevent skin or eye contact
Refer to supplier-provided SDS for detailed guidance
4-(4-Phenylbutoxy)benzoic Acid (CAS 30131-16-9) plays an essential role in:
Pharmaceutical innovation
Functional material development
Fine chemical manufacturing
Academic organic chemistry studies
Its unique structural features make it a reliable intermediate for industries that require precision, purity, and performance.
30131-16-9 (4-(4-Phenylbutoxy)benzoic Acid) is a valuable and versatile chemical intermediate with wide-ranging applications in pharmaceuticals, materials science, and research. Its dual aromatic structure and functional groups make it a preferred choice for developing complex organic compounds and high-performance materials.