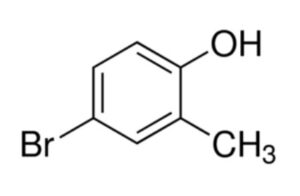
4-Bromo-2-methylphenol (CAS 2362-12-1) is an important organic compound widely used in pharmaceutical synthesis, agrochemical development, and advanced chemical research. Its unique brominated phenolic structure makes it highly valuable as an intermediate in producing biologically active molecules and fine chemicals.
This article provides a detailed overview of the properties, uses, and industrial relevance of 4-Bromo-2-methylphenol.
4-Bromo-2-methylphenol is a brominated derivative of methylphenol, combining the reactivity of a phenolic group with the functional versatility of a bromide substituent. It serves as a key building block for chemical synthesis, especially where selective bromination and aromatic substitution play a crucial role.
Its CAS number 2362-12-1 makes it easily identifiable across chemical catalogs and industrial applications.
Property |
Details |
|---|---|
CAS Number |
2362-12-1 |
Chemical Name |
4-Bromo-2-methylphenol |
Molecular Formula |
C₇H₇BrO |
Molecular Weight |
187.03 g/mol |
Appearance |
Off-white to light brown solid |
Functional Groups |
Phenol group, bromine substituent |
Its combination of aromaticity, phenolic OH group, and bromine atom allows it to engage in various organic reactions, including substitution, coupling, and esterification.
4-Bromo-2-methylphenol is used across several industries due to its strong chemical reactivity and versatility.
The compound is widely used as an intermediate in synthesizing:
Antibacterial agents
Anti-inflammatory drugs
Enzyme inhibitors
Specialized heterocyclic molecules
Its bromine atom serves as a reactive site for Suzuki, Heck, and Sonogashira coupling reactions, enabling the creation of complex drug molecules.
4-Bromo-2-methylphenol is employed in producing:
Fungicides
Herbicide intermediates
Insecticidal compounds
Its phenolic structure contributes to strong biological activity, making it ideal for developing plant-protection chemicals.
Chemists also use this compound for:
Aromatic substitution reactions
Preparation of custom organic intermediates
Synthesis of dyes and pigments
Research-driven chemical modifications
The phenolic group allows for ester or ether formation, greatly expanding its synthetic flexibility.
Although used in smaller quantities, it helps in:
Specialty polymer modification
Synthesis of resin additives
Preparation of functional monomers
Its rigid aromatic structure contributes to stability and enhanced material properties.
4-Bromo-2-methylphenol is valued because of:
The combination of phenolic OH and bromine provides multiple reaction pathways.
Useful across pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, polymers, and academic research.
Ensures consistent performance in creating high-purity organic intermediates.
Efficient reactions mean lower production costs and reduced waste.
Because of these advantages, industries rely on this compound to maintain scalable, efficient production of complex molecules.
To maintain quality and safety:
Store in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area
Keep away from heat, oxidizing agents, and strong bases
Use gloves, goggles, and lab coats during handling
Avoid inhalation of dust or fumes
Refer to the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for full guidance
Proper storage helps prevent degradation of the phenolic and brominated functionalities.
4-Bromo-2-methylphenol (2362-12-1) is a highly valuable intermediate with significant applications in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and fine chemical synthesis. Its chemical versatility and reactivity make it essential for industries developing advanced organic compounds.
Whether used for drug development or specialty chemicals, this compound plays a vital role in modern synthesis.