Triethyl Phosphite (CAS 122-52-1) is a key organophosphorus compound widely used in chemical synthesis, polymer production, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and industrial processes. Known for its versatility, reactivity, and efficiency as a reducing and phosphorylating agent, Triethyl Phosphite plays an important role across multiple industries.
This article explores its chemical properties, applications, benefits, and industrial importance in modern chemical science.
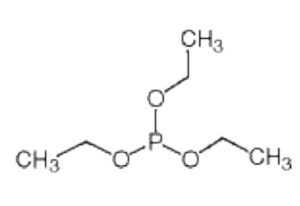
Triethyl Phosphite is an organophosphate ester with the formula P(OEt)₃. It belongs to the phosphite family and is widely used as:
A reagent in organic synthesis
An intermediate for producing chemicals
A ligand in coordination chemistry
A stabilizer for polymers
Because of its strong nucleophilicity and ability to donate phosphorus, Triethyl Phosphite is an essential raw material in research and large-scale industrial production.
Property |
Details |
|---|---|
CAS Number |
122-52-1 |
Chemical Formula |
C₆H₁₅O₃P |
Molecular Weight |
166.15 g/mol |
Appearance |
Colorless to pale yellow liquid |
Odor |
Mild, characteristic |
Boiling Point |
~156–158°C |
Flash Point |
~66°C |
Solubility |
Soluble in organic solvents |
Its attractive physical profile, including moderate boiling point and high reactivity, makes it suitable for controlled reactions in laboratory and industrial conditions.
Triethyl Phosphite is exceptionally versatile. Some of its key applications include:
Triethyl Phosphite is a widely used reagent in organic chemistry, mainly due to its ability to:
Act as a reducing agent
Participate in the Arbuzov reaction
Assist in creating phosphorus-containing intermediates
It helps synthesize various fine chemicals, intermediates, and complex organic compounds.
In medicinal chemistry, Triethyl Phosphite plays a role in producing:
API intermediates
Antiviral compounds
Bioactive molecules
Heterocyclic structures
Pharmaceutical manufacturers prefer it for its high efficiency and clean reaction profiles.
Triethyl Phosphite is used as:
A stabilizer in PVC production
An antioxidant in polymer processing
A flame retardant intermediary
It ensures improved durability, color stability, and heat resistance in plastics.
Triethyl Phosphite is a key ingredient in synthesizing pesticides, fungicides, and plant growth regulators. It provides:
Chemical stability
Effective phosphorylation reactions
Compatibility with various active ingredients
Its ability to bind metals makes it a useful ligand for forming:
Metal complexes
Catalysts
Organometallic compounds
These complexes are essential in catalysis and research-based chemistry.
Triethyl Phosphite stands out due to its:
Its strong nucleophilic phosphorus atom makes it suitable for large-scale chemical transformations.
From pharmaceuticals to polymers, it fits into many industrial workflows.
Efficient reactions and wide availability result in lower production costs.
Its moderate stability allows safe handling, storage, and transportation.
Triethyl Phosphite supports processes vital for making everyday products—from plastics to medicines.
For safe use:
Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area
Keep away from moisture, air, and strong oxidizers
Use proper PPE (gloves, goggles, lab coat)
Handle under inert atmosphere for sensitive reactions
Always refer to the supplier’s Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for detailed guidance.
Triethyl Phosphite (122-52-1) remains one of the most valuable organophosphorus reagents in chemical science. Its contribution spans organic synthesis, pharmaceuticals, polymer manufacturing, and industrial chemistry.
Its unique reactivity, reliability, and multifunctional nature ensure its continued importance in both research laboratories and industrial environments.