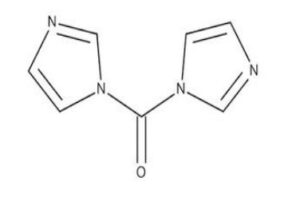
1,1′-Carbonyldiimidazole (commonly known as CDI) is one of the most widely used coupling and activation reagents in organic and peptide chemistry. Known for its efficiency, mild reaction conditions, and broad compatibility, CDI has become a staple in pharmaceutical synthesis, biochemical research, and industrial manufacturing.
This article provides a detailed overview of its structure, properties, applications, advantages, and market relevance in 2025.
CDI (CAS 530-62-1) is an organic reagent derived from imidazole. It is primarily used to activate carboxylic acids for nucleophilic substitution reactions, making it a versatile chemical in synthesis laboratories and industrial setups.
Chemical Name: 1,1′-Carbonyldiimidazole
CAS Number: 530-62-1
Molecular Formula: C₇H₆N₄O
Molecular Weight: 162.14 g/mol
Appearance: White to off-white crystalline powder
Solubility: Soluble in THF, acetonitrile, DMF, DMSO
CDI is a carbonyl-transfer reagent that reacts with carboxylic acids to form highly reactive acyl imidazolides. These intermediates can then react with amines, alcohols, or thiols to form:
Amides
Esters
Peptides
Carbamates
Operates under mild, moisture-sensitive but stable conditions
Produces minimal toxic by-products (mainly imidazole)
Compatible with a wide range of functional groups
Highly efficient for solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS)
CDI plays a critical role in the manufacturing of:
API intermediates
Peptide-based drugs
Heterocyclic drug components
Its clean reaction profile reduces purification complexity, making it ideal for large-scale pharmaceutical processes.
One of the most well-known uses of CDI is in peptide coupling.
CDI offers:
High yield
Low racemization
No need for strong bases
This makes it preferred for both research-level peptide synthesis and industrial peptide manufacturing.
CDI transforms alcohols and amines into:
Esters (via activated acyl imidazolides)
Carbamates (from amines + carbon dioxide)
The clean reaction pathways make CDI valuable in:
Polymer chemistry
Agrochemical intermediate synthesis
Specialty chemical manufacturing
CDI is used routinely in:
Modification of biomolecules
Enzyme immobilization
Surface functionalization
Preparation of labeled compounds
Its efficiency and compatibility with sensitive molecules make it ideal for bioscience applications.
Traditional coupling agents like DCC or EDC often produce problematic by-products or require harsh conditions. CDI offers several advantages:
These benefits have positioned CDI as a modern, reliable coupling reagent in 2025.
While CDI is considered relatively user-friendly, it is moisture-sensitive and requires proper handling.
Use gloves, goggles, and a lab coat
Avoid exposure to moisture or humidity
Work in a well-ventilated area or fume hood
Store in a cool, dry place
Keep containers tightly sealed
Use desiccants if necessary
The increasing demand for peptide therapeutics, small-molecule APIs, and bioconjugation technologies is driving the global CDI market upward.
Rising adoption of SPPS in drug discovery
Expansion of peptide-based drugs
Increased R&D spending in biotech
Industrial shift toward cleaner, safer reagents
Asia-Pacific (India & China dominate production)
Europe (high R&D usage)
United States (biotech and pharmaceutical research centers)
CDI is expected to grow steadily as industries continue replacing older coupling reagents with more efficient and cleaner alternatives.
1,1′-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI, CAS 530-62-1) is a powerful and highly reliable reagent that plays a central role in modern organic synthesis, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and peptide chemistry. Its broad utility, safety profile, and efficiency make it indispensable for both research laboratories and industrial production facilities.